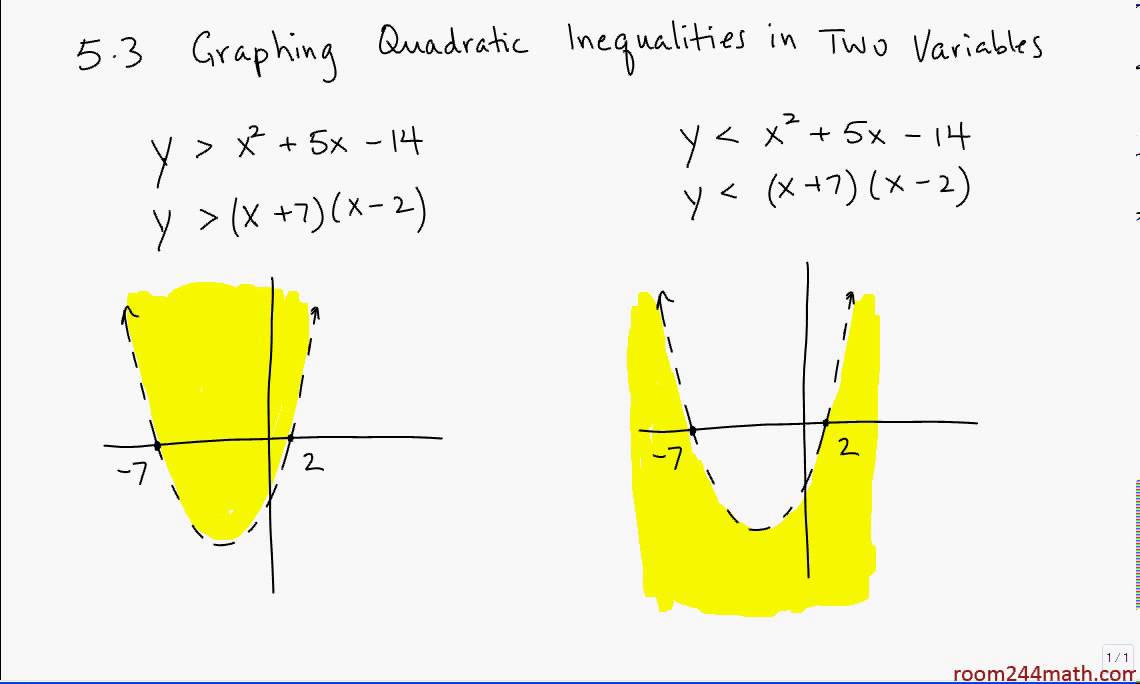
5.3 Graphing Quadratic Inequalities in Two Variables YouTube
It is important to note that this quadratic inequality is in standard form, with zero on one side of the inequality. Step 1: Determine the critical numbers. For a quadratic inequality in standard form, the critical numbers are the roots. Therefore, set the function equal to zero and solve. − x2 + 6x + 7 = 0.
How to Graph a Quadratic Inequality with 2 Variables Algebra
The difference between a quadratic equation and a quadratic inequality is that the quadratic equation is equal to some number while quadratic inequality is either less than or greater than some number. Some examples of quadratic inequalities in one variable are: + x - 1 > 0. + 2x - 1 < 0. The standard form of quadratic inequalities in one.

Algebra 1 Worksheets Quadratic Functions Worksheets Quadratics, Quadratic functions
A quadratic inequality is one that includes an x^{2} term and thus has two roots, or two x-intercepts. This results in a parabola when plotting the inequality on a coordinate plane. Solving an inequality means finding the values of x that.
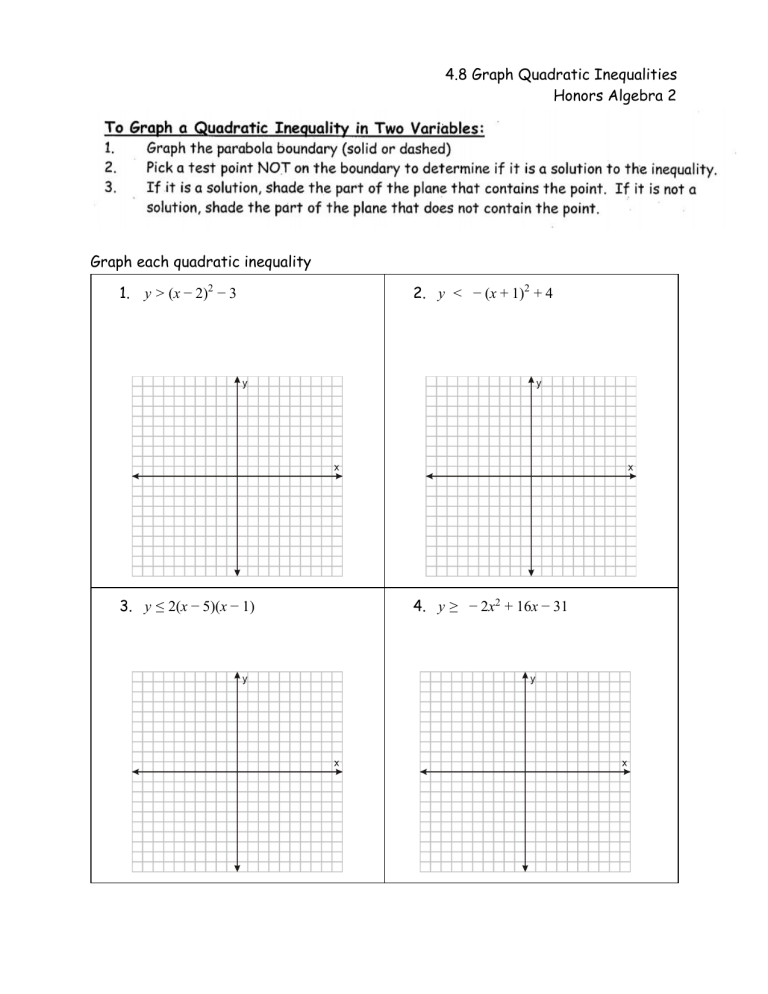
4.8 graph quadratic inequalities
I make short, to-the-point online math tutorials. I struggled with math growing up and have been able to use those experiences to help students improve in ma.
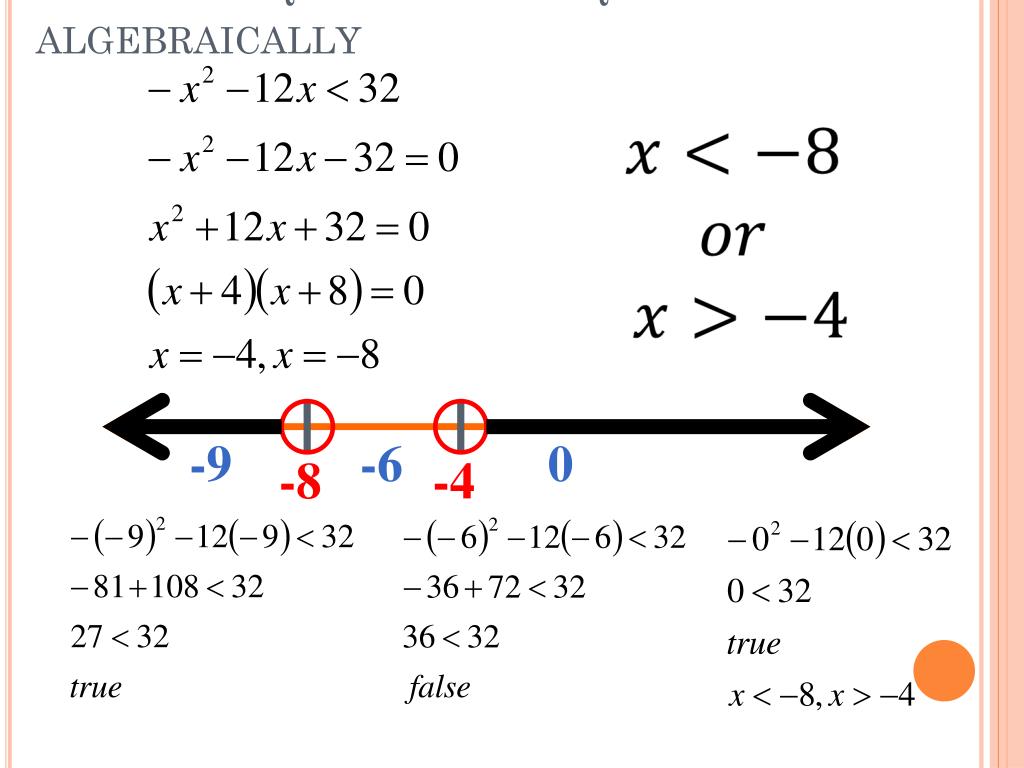
PPT 4.9 Solving Quadratic Inequalities PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4887323
To solve a quadratic inequality ax² + bx + c > d: Draw the line y = d. Determine the points where the parabola ax² + bx + c crosses/touches this line. To find them, solve ax² + bx + (c - d) = 0. If there's no solution, your parabola is entirely above or below the line. Graph the parabola, taking into account the results from Step 2: The arms.

Math Principles Graphs of Quadratic Inequalities
This is a cubic equation (the highest exponent is a cube, i.e. x 3), and is hard to solve, so let us graph it instead: The zero points are approximately: −1.1; 1.3; 2.9; And from the graph we can see the intervals where it is greater than (or equal to) zero: From −1.1 to 1.3, and; From 2.9 on; In interval notation we can write:
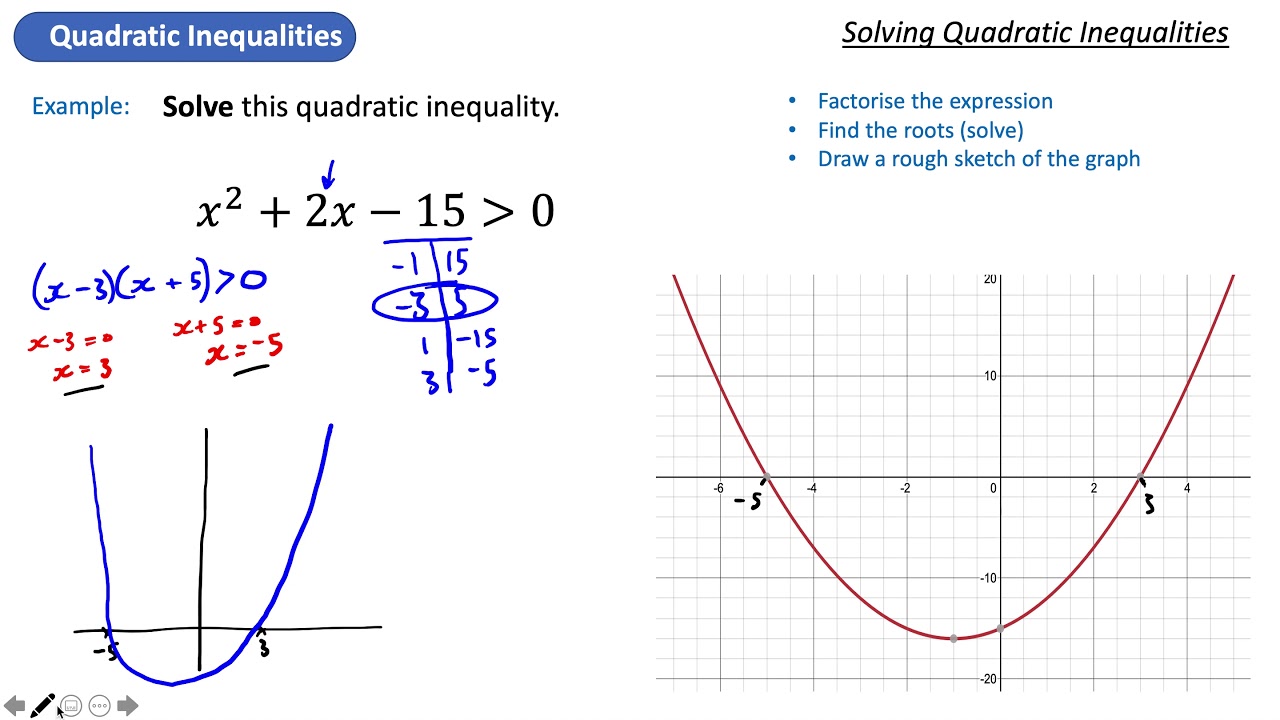
Solving Quadratic Inequalities YouTube
The Graph of a Quadratic Function. A quadratic function is a polynomial function of degree 2 which can be written in the general form, f(x) = ax2 + bx + c. Here a, b and c represent real numbers where a ≠ 0 .The squaring function f(x) = x2 is a quadratic function whose graph follows. Figure 6.4.1.
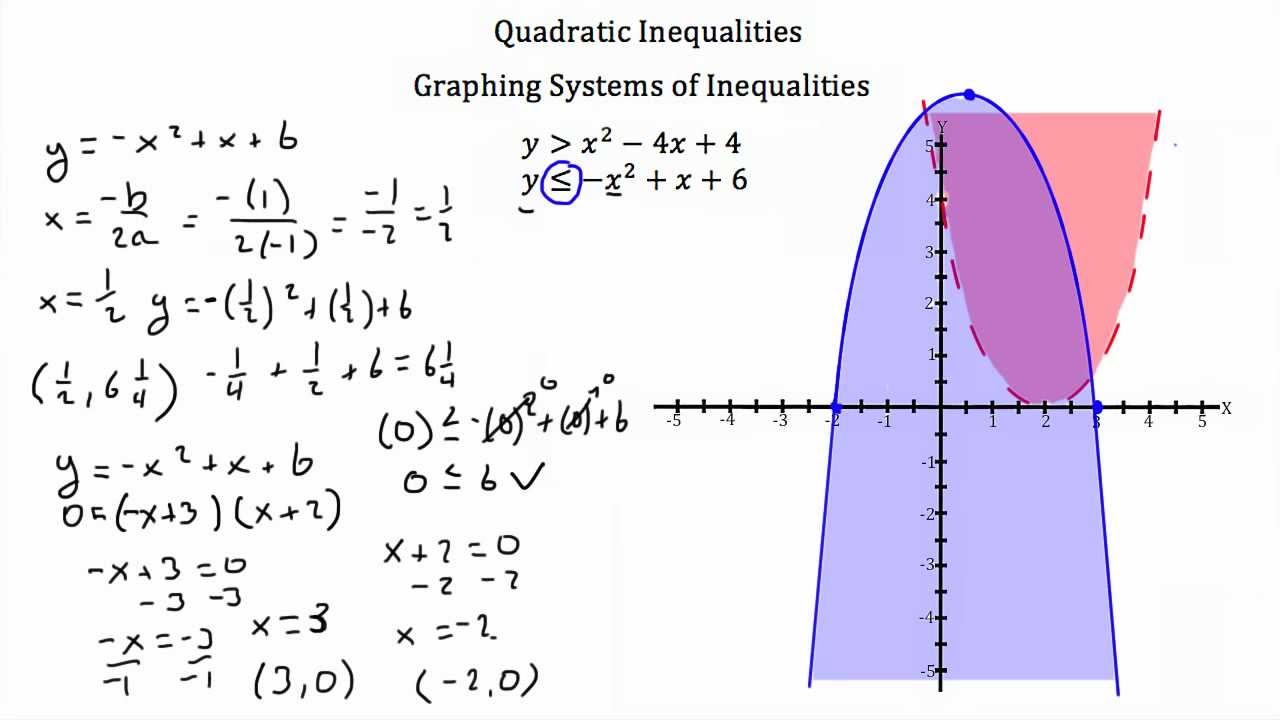
Inequalities with Quadratic Functions YouTube
A quadratic inequality is an inequality that contains quadratic terms. Recall that a quadratic polynomial is a polynomial of degree 2 and is generally written as {eq}f (x) = ax^2+bx+c {/eq}. In.

Defining quadratic inequalities and graphing their intervals
The same basic concepts apply to quadratic inequalities like $$ y x^2 -1 $$ from digram 8. This is the same quadratic equation, but the inequality has been changed to $$ \red $$. In this case, we have drawn the graph of inequality using a pink color. And that represents the graph of the inequality.

Graph and Solve Quadratic Inequalities Section 4 9 YouTube
The graph will highlight in green the regions where the graph is above or below zero. Hide/unhide the folders above to switch between the two inequalities. Use the sliders to adjust the values of a, b and c in the quadratic. The red lines will highlight the values of x which correspond to the inequality.
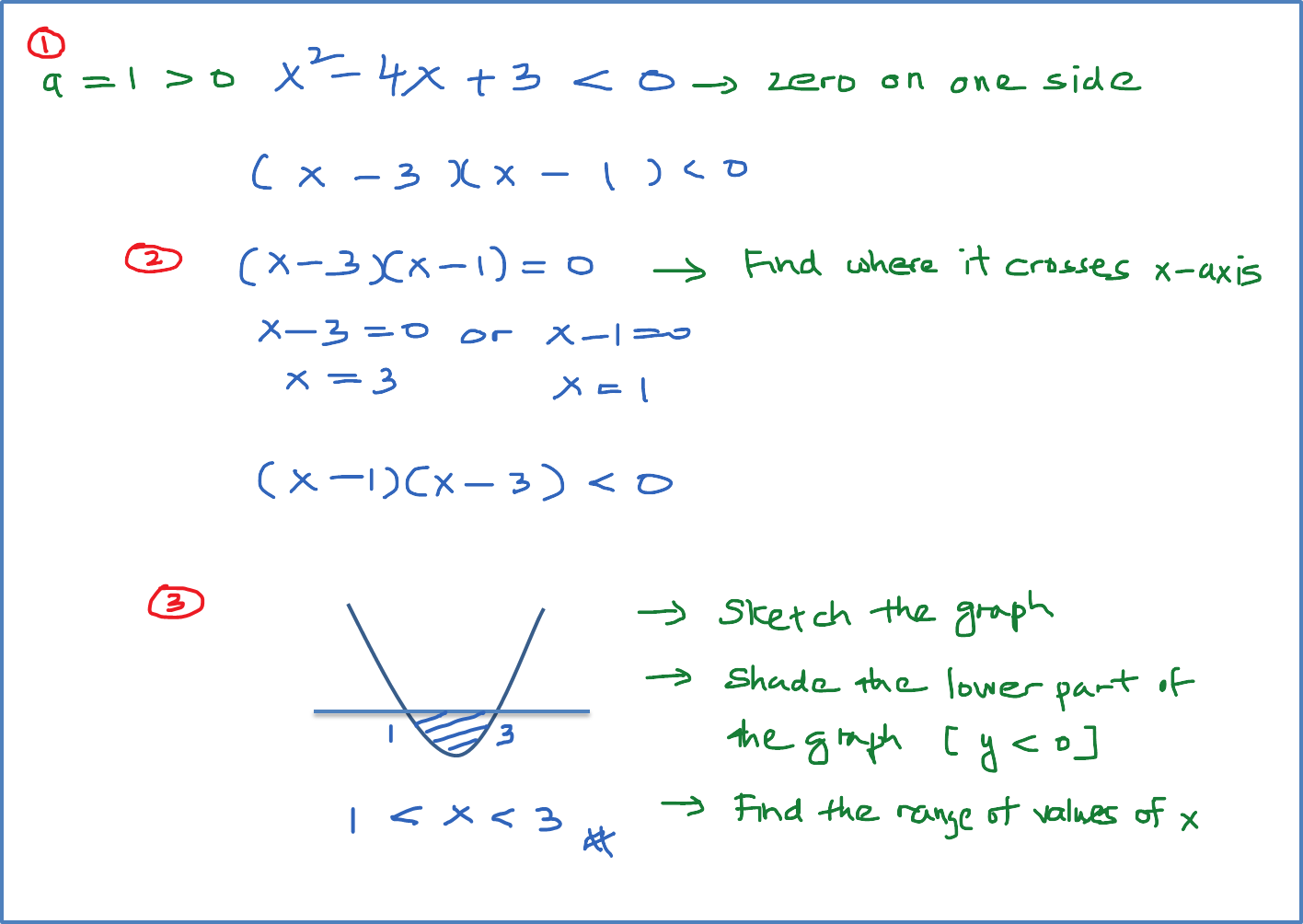
3.6 Quadratic Inequalities SPM Additional Mathematics
Write the quadratic inequality in standard form. Graph the function \(f(x)=ax^{2}+bx+c\). Determine the solution from the graph. In the last example, the parabola opened upward and in the next example, it opens downward. In both cases, we are looking for the part of the parabola that is below the \(x\)-axis but note how the position of the.
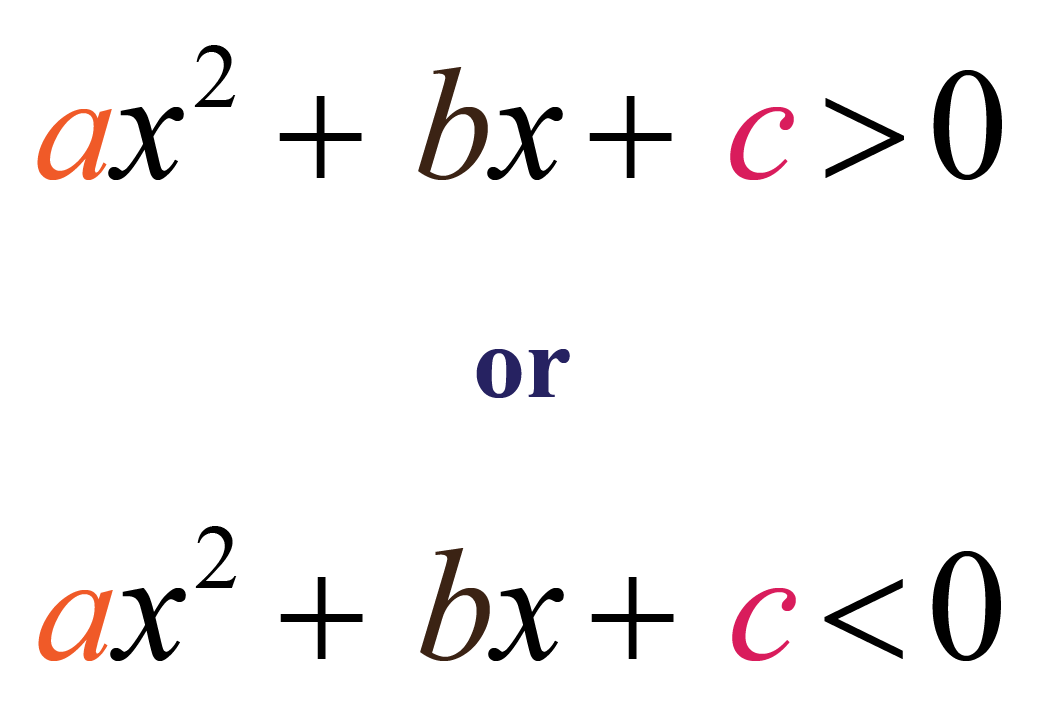
Quadratic Inequalities Graphs Calculator Solved Examples Cuemath
The second inequality is y is less than 2x minus 5. So if we were to graph 2x minus 5, and something already might jump out at you that these two are parallel to each other. They have the same slope. So 2x minus 5, the y-intercept is negative 5. x is 0, y is negative 1, negative 2, negative 3, negative 4, negative 5.

Solve Quadratic Inequalities Intermediate Algebra
Explore math with our beautiful, free online graphing calculator. Graph functions, plot points, visualize algebraic equations, add sliders, animate graphs, and more. Quadratic Inequalities. Save Copy. Log InorSign Up. x 2 − 5 x − 6. 1. x 2 − 5 x − 6 > 0. 2. x 2 − 5 x.
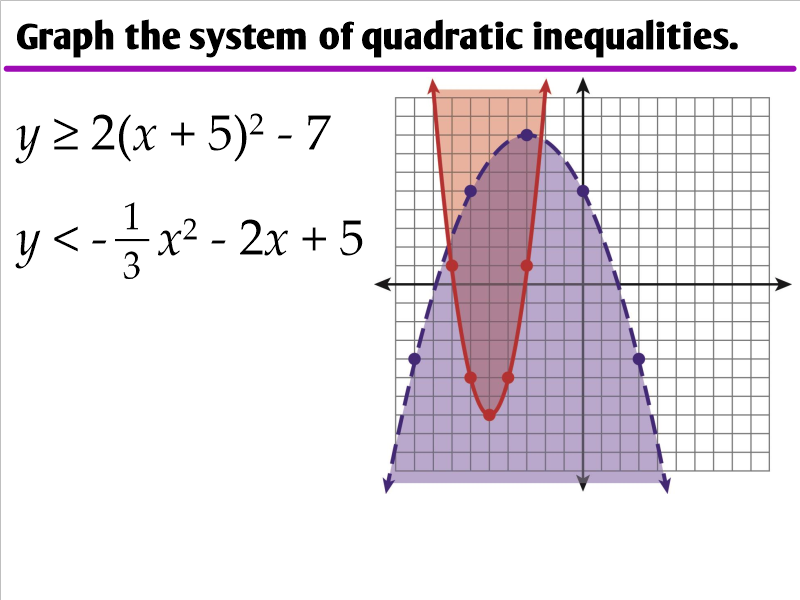
4.6 Graphing Quadratic Inequalities Ms. Zeilstra's Math Classes
Video transcript. Welcome to the presentation on quadratic inequalities. Before we get to quadratic inequalities, let's just start graphing some functions and interpret them and then we'll slowly move to the inequalities. Let's say I had f of x is equal to x squared plus x minus 6.
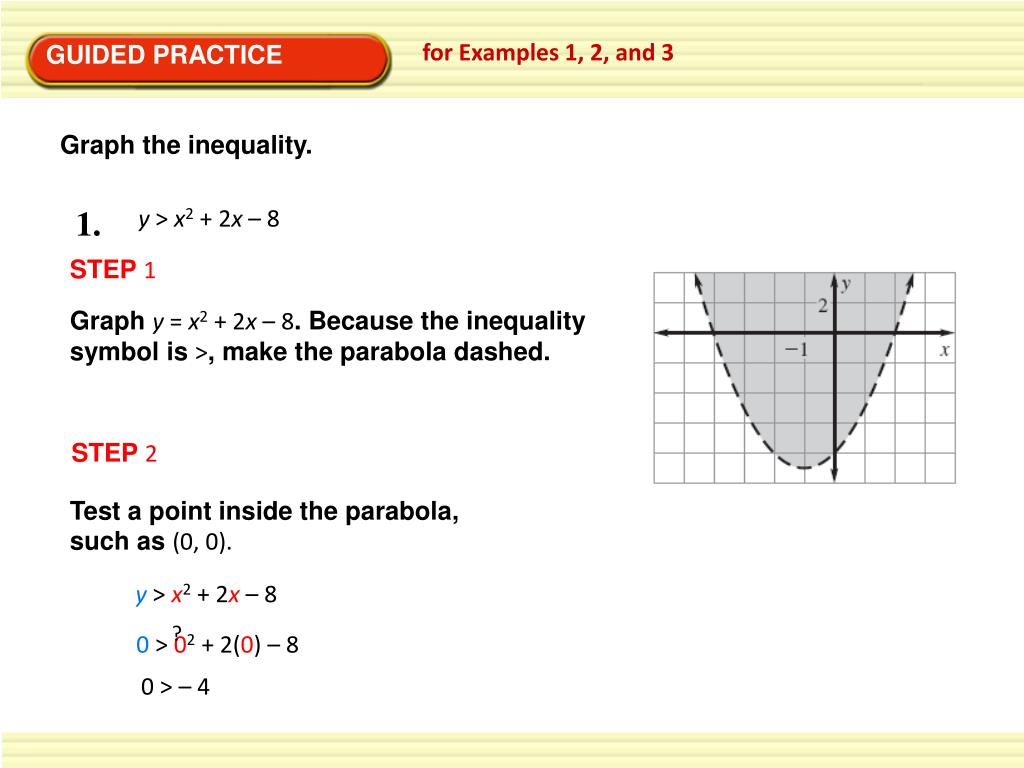
PPT Graphing Quadratic Inequalities PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1892142
How do you solve quadratic inequalities? To solve a quadratic inequality write the inequality in the standard form ax^2 + bx + c < 0 or ax^2 + bx + c > 0, find the roots of the quadratic equation. Use the roots to divide the number line into intervals. Determine the sign of the expression in that interval.
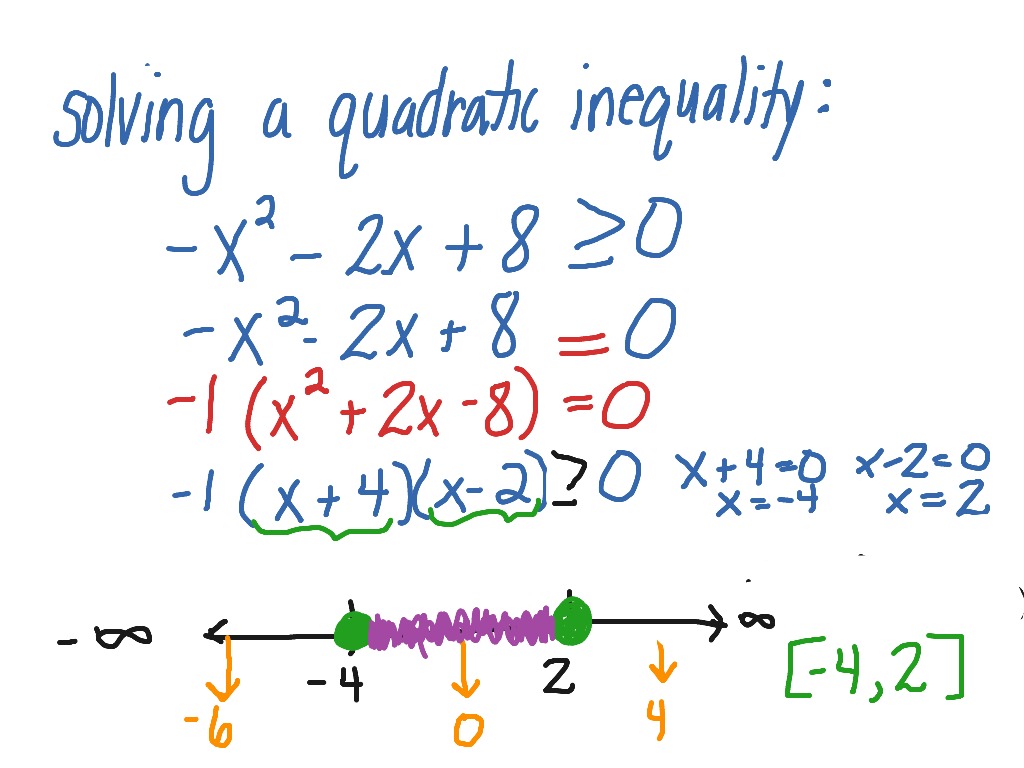
Solving a quadratic inequality (negative in front) Math, Quadratic Inequalities ShowMe
You can use the quadratic equation to find the endpoints of the intervals that will be you solution, and would then need to test in which of those intervals the inequality is true. So in this case you could use it to find -5 and 2 [ (-3 +- Sqrt (9+4 (10)1))/2 = (-3 +- 7)/2 = -10/2 or 4/2]. This breaks up the number line into 3 intervals {x<-5.